Domain Eukaryota |
|
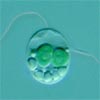 |
The Glaucophyta are a small kingdom of freshwater algae. Like other Archeoplastida, they have chloroplasts surrounded by two membranes, the remains of directly absorbed symbiotic cyanobacteria. |
The Glaucophyta (like many Green Algae) have two flagella of unequal length, sometimes covered with fine hairs. These are controlled by a layered microtubule structure. They have flat mitochondria and reproduce by splitting, with two identical sets of chromosomes (mitosis). The kingdom's name comes from glauco-, "bluish-green". They are sometimes called Glaucocystophyta or Glaucocystids.There are three groups:
The Glaucophyta branched off early from the super-kingdom Archeoplastida and are interexting for scientists studying the origins of the Land Plants and Green Algae.
|
|
| (close window) | |